Researches
Evolution of Martian interior and surface environment
Mars is a planet closest to teh Earth taht satisfies the condition of existence of life. Our knowledge about Mars has improved dramatically in recent years owing to the Mars exploration missions conducted by NASA and ESA, as well as the analyses of Martian meteorites. We investigate the evolution of the Martian mantle and crust and their interaction with the surface environment by mean of chemical and isotopic analyses of Martian meteorites.
Related papers
Moriwaki, R.., Usui, T., Tobita, M., Yokoyama, T.
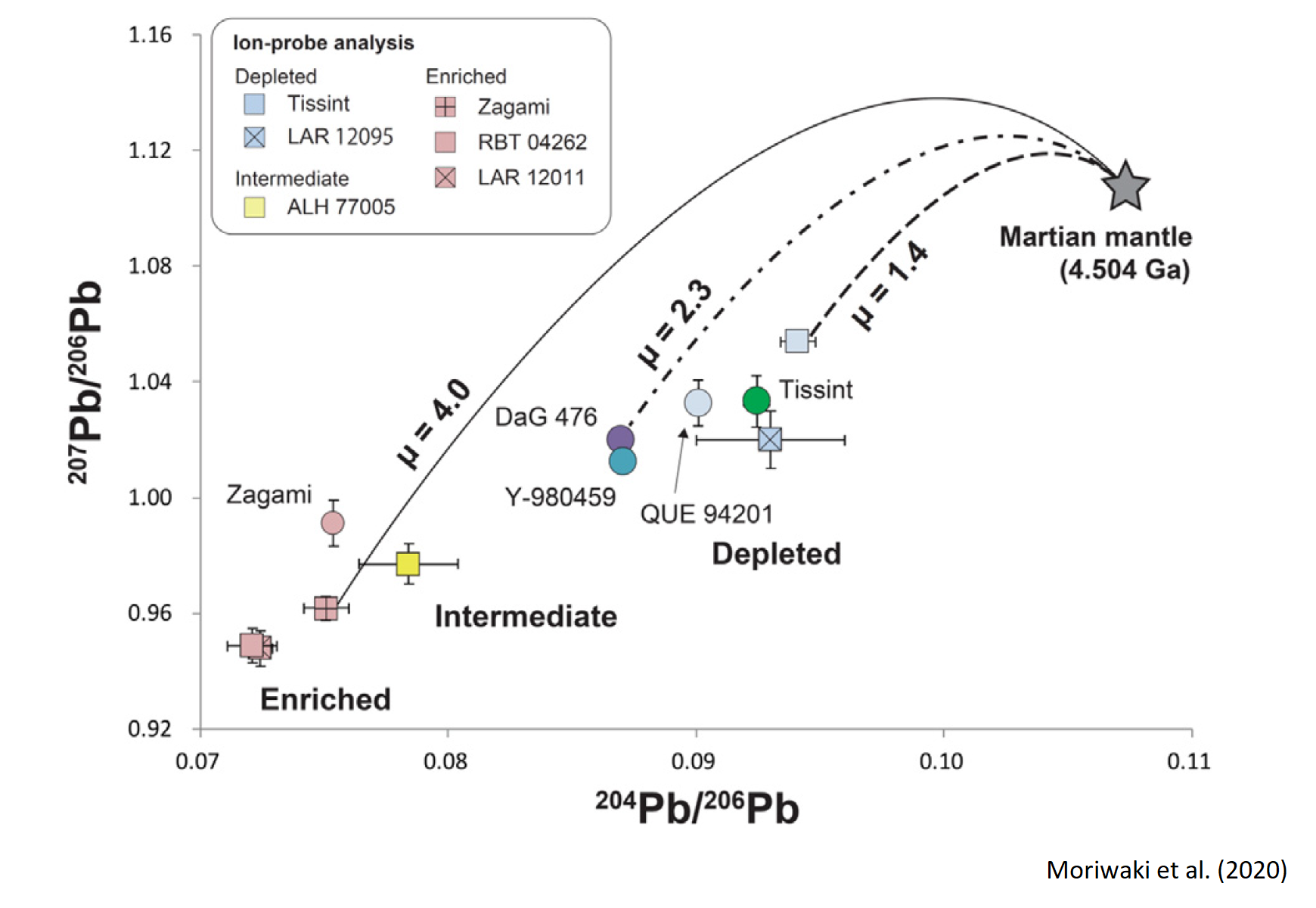
Geochemically heterogeneous Martian mantle inferred from Pb isotope systematics of depleted shergottites.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 274, 157-171, 2020.
Moriwaki, R., Usui, T., Simon, J.I., Jones, J.H., Yokoyama, T. and Tobita, M.
Coupled Pb isotopic and trace element systematics of Tissint meteorite: geochemical signatures of the depleted shergottite source mantle.
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 474, 180-189, 2017.
Tobita, M., Usui, T. and Yokoyama, T.
New Constraints on Shergottite petrogenesis from analysis of Pb isotopic compositional space: implications for mantle heterogeneity and crustal assimilation on Mars.
Geochemical Journal, 51 (1), 81-94, 2017.